Introduction
Vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. These essential nutrients are required in small quantities but have a significant impact on our bodily functions. Among these vitamins, Vitamin B12 stands out as a powerhouse, responsible for numerous vital processes in the body. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of Vitamin B12, exploring its properties, functions, dietary sources, absorption and metabolism, deficiency, diagnosis, treatment, and much more. Get ready to unveil the secrets of this remarkable vitamin that plays a pivotal role in our everyday lives.
Understanding Vitamin B12

What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin belonging to the B-complex family. It is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system, the formation of red blood cells, and the synthesis of DNA. Unlike other B vitamins, which can be synthesized by certain microorganisms in our bodies, Vitamin B12 is obtained exclusively from external sources.
Properties and Chemical Composition of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a complex molecule with a unique structure. It consists of a central cobalt atom surrounded by a tetrapyrrole ring system, making it a cobalamin compound. This complex structure is what enables the vitamin to carry out its physiological functions effectively.

Key Functions and Benefits of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 plays a pivotal role in various vital functions of the body, including:
- DNA Synthesis: Vitamin B12 is crucial for the synthesis of DNA, the genetic material found in our cells. This process is fundamental for the proper growth, development, and maintenance of bodily tissues.
- Red Blood Cell Formation: Vitamin B12 aids in the formation of healthy red blood cells. It works in conjunction with other B vitamins, such as folate, to promote the production of red blood cells essential for oxygen transport.
- Nervous System Function: Vitamin B12 supports the proper functioning of the nervous system. It helps maintain the protective coating (myelin sheath) around nerve fibers, facilitating efficient transmission of nerve signals.
- Energy Production: This mighty vitamin plays a crucial role in converting the food we eat into usable energy. It helps metabolize carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, ensuring our bodies have a steady supply of energy.
- Cell Division and Growth: Vitamin B12 is necessary for cell division and growth, making it particularly important during periods of rapid growth, such as childhood, adolescence, and pregnancy.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin B12
Obtaining adequate Vitamin B12 from various dietary sources is crucial for meeting our daily requirements. Let’s explore both animal-based and plant-based sources of this vitamin.
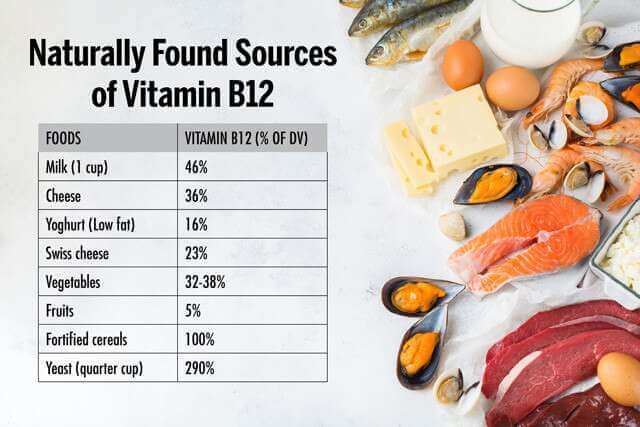
Animal-Based Sources
- Meat and Poultry: Animal meats, such as beef, chicken, and pork, are excellent sources of Vitamin B12. They provide high bioavailable forms of the vitamin, ensuring efficient absorption and utilization by the body.
- Fish and Seafood: Fatty fish like salmon, trout, and tuna are not only rich in omega-3 fatty acids but also contain substantial amounts of Vitamin B12. Shellfish, such as clams and mussels, are other excellent sources.
- Dairy and Eggs: Dairy products, including milk, cheese, and yogurt, are valuable sources of Vitamin B12. Additionally, eggs, especially the yolk, contain significant amounts of this essential nutrient.
Plant-Based Sources
- Fortified Foods: Many plant-based food products, such as breakfast cereals, plant-based milk alternatives (soy, almond), and nutritional yeast, are fortified with Vitamin B12. These fortified foods are essential for individuals following a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle.
- Algae and Seaweed: Certain types of algae and seaweed, like nori and spirulina, also contain Vitamin B12. However, their bioavailability and absorption rates can vary, so it’s important to consider other sources as well.
Exploring and incorporating these dietary sources into our meals ensures an adequate intake of Vitamin B12 and supports our overall health.
Absorption and Metabolism of Vitamin B12
Understanding how Vitamin B12 gets absorbed and utilized in our bodies provides insights into its efficient utilization and prevention of deficiency.
Digestion Process of Vitamin B12
- Stomach: In the stomach, Vitamin B12 gets released from food through the action of digestive enzymes. It then binds with proteins called R-binders or haptocorrins, preventing its degradation by stomach acids.
- Small Intestine: Further down the digestive tract, in the small intestine, Vitamin B12 is released from R-binders. It then combines with the intrinsic factor, a glycoprotein released by stomach cells. This intrinsic factor is essential for the absorption of Vitamin B12.
Intrinsic Factor: The Key Player in Absorption
Intrinsic factor plays a crucial role in the absorption of Vitamin B12. It forms a complex with the vitamin, allowing it to be recognized and efficiently absorbed by receptor sites in the terminal ileum, a portion of the small intestine. This intricate mechanism ensures optimal absorption and utilization of Vitamin B12 in the body.
Transport and Utilization of Vitamin B12 in the Body
Once absorbed, Vitamin B12 binds with a protein called transcobalamin II (TCII) for transport. This complex protects the vitamin and allows it to be carried to various tissues and organs throughout the body. Cells utilize Vitamin B12 for important physiological processes, such as DNA synthesis, energy production, and nervous system function.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can have serious consequences on our health. Understanding its causes, recognizing the signs and symptoms, and being aware of the potential long-term health consequences is essential.

Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to Vitamin B12 deficiency, including:
- Inadequate Dietary Intake: A diet lacking in animal-based products and fortified foods can lead to Vitamin B12 deficiency, especially among individuals following strict vegetarian or vegan diets.
- Digestive Disorders: Certain digestive disorders, such as pernicious anemia, can impair the production of intrinsic factor, hindering the absorption of Vitamin B12.
- Age: As we age, our ability to absorb Vitamin B12 from food decreases. Therefore, older adults are more prone to deficiency.
- Medications: Some medications, such as certain diabetes drugs and antacids, can interfere with the absorption and utilization of Vitamin B12.
Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
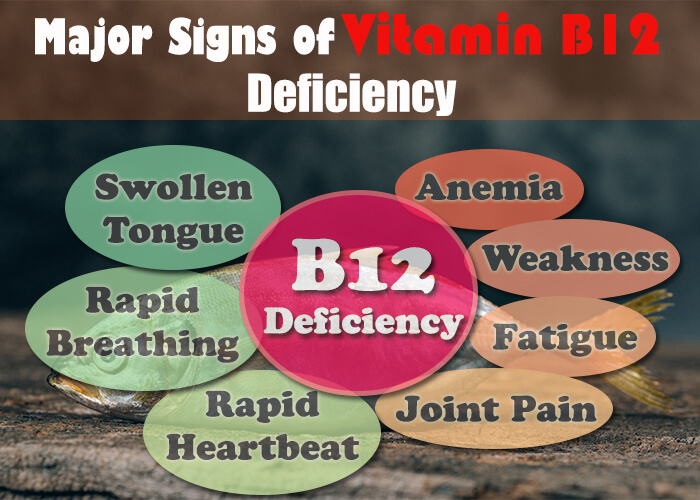
Early detection and recognition of the signs and symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency are crucial for prompt intervention. Common signs include:
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Pale or Yellowish Skin
- Shortness of Breath
- Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet
- Memory Loss or Cognitive Difficulties
- Mood Changes and Depression
Long-term Health Consequences
If left untreated, Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to serious complications. These may include irreversible nerve damage, megaloblastic anemia, cardiovascular complications, and potentially adverse effects on cognitive and mental health.
Diagnosing and Treating Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Timely diagnosis of Vitamin B12 deficiency is essential for effective treatment. Medical professionals employ various diagnostic tests to assess deficiency levels accurately.
Diagnostic Tests for Deficiency
Common diagnostic tests for Vitamin B12 deficiency include:
- Blood Tests: These measure the levels of Vitamin B12 in the blood. Other related markers, such as homocysteine and methylmalonic acid levels, may also be evaluated.
- Intrinsic Factor Antibody Test: This test helps determine whether an individual has an autoimmune condition that interferes with the production or function of the intrinsic factor.
Dietary Supplements and Injections
Supplementation through dietary supplements or injections is often necessary to treat Vitamin B12 deficiency effectively. Oral supplements or injections bypass the need for intrinsic factors and provide Vitamin B12 directly to the body.
Lifestyle Modifications to Optimize Vitamin B12 Levels
In addition to supplements, making certain lifestyle modifications can help optimize Vitamin B12 levels naturally. These include:
- Increasing intake of animal-based sources, fortified foods, and nutritional yeast.
- Sensible exposure to sunlight boosts Vitamin B12 synthesis in the skin.
- Managing underlying digestive disorders that may hinder absorption.
Special Considerations for Vitamin B12
Understanding specific considerations related to Vitamin B12 is crucial for targeted interventions and maintaining optimal health.
Vitamin B12 Requirements for Different Age Groups
The recommended daily dosage of Vitamin B12 varies depending on age:
- Infants (0-6 months): 0.4 micrograms (mcg)
- Infants (7-12 months): 0.5 mcg
- Children (1-3 years): 0.9 mcg
- Children (4-8 years): 1.2 mcg
- Adolescents (9-13 years): 1.8 mcg
- Adults (including pregnant and breastfeeding women): 2.4 mcg
Vitamin B12 Absorption in Pregnant Women
Pregnant women have increased Vitamin B12 requirements to support fetal development. Ensuring an adequate intake through a balanced diet and supplements is vital for both the mother and the unborn child.
Vitamin B12 and Vegetarian/Vegan Diets
Vegetarians and vegans, particularly strict ones who avoid all animal products, must pay close attention to their Vitamin B12 intake. Fortified foods and supplements are essential to meet their daily requirements.
Link between Vitamin B12 and Health Conditions
Vitamin B12 plays a significant role in the prevention and management of various health conditions. Let’s explore its association with specific conditions:
Vitamin B12 and Anemia
Vitamin B12 is vital for the production of healthy red blood cells. Deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia, where red blood cells become large and dysfunctional, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and other related symptoms.
Vitamin B12 and Cognitive Health
Emerging research suggests that Vitamin B12 may have a beneficial impact on cognitive health, particularly in aging populations. Adequate levels of Vitamin B12 ensure optimal brain function, memory, and overall cognitive performance.
Vitamin B12 and Mental Health Disorders
Studies have indicated a possible link between Vitamin B12 deficiency and mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. While further research is needed to establish a clear cause-and-effect relationship, maintaining adequate Vitamin B12 levels is essential for overall mental well-being.
Emerging Research on Vitamin B12
Scientific studies on Vitamin B12 are constantly evolving, shedding light on new findings and innovations in supplementation.
Scientific Studies and Findings
Ongoing research suggests potential links between Vitamin B12 and other health conditions, including cardiovascular health, bone health, and immune function. Additionally, studies explore the role of Vitamin B12 in modulating gene expression and its potential as a therapeutic tool in various diseases.
Innovations in Vitamin B12 Supplementation
Researchers are exploring innovative methods of Vitamin B12 administration, such as transdermal patches and nasal sprays. These advancements aim to enhance bioavailability and ease of use for individuals with specific needs or difficulties with traditional supplementation methods.
Summary and Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is a vital nutrient that plays a central role in numerous bodily functions. From red blood cell formation to energy production and nervous system function, its impact on our health is undeniable. Understanding the dietary sources, absorption process, and potential consequences of deficiency allows us to take proactive measures to maintain optimal Vitamin B12 levels. Whether you are a meat-eater, vegan, young or old, incorporating suitable sources into your diet, considering supplements when necessary, and staying informed about emerging research will empower you to unleash the powerhouse benefits of Vitamin B12.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A. Can Vitamin B12 be harmful?
Vitamin B12 is considered safe when taken within recommended dosages. However, extremely high doses can cause adverse effects in some individuals, such as acne, diarrhea, or allergic reactions. It is crucial to follow proper dosage guidelines and consult a healthcare professional if concerns arise.
B. Is it possible to get too much Vitamin B12?
While rare, excessive intake of Vitamin B12 can occur through supplementation. However, the body has effective mechanisms to regulate its absorption, utilization, and elimination. Nonetheless, moderation is key, and it is always advisable to follow recommended dosages.
C. Can Vitamin B12 improve energy levels?
Vitamin B12 is involved in energy production by assisting in the metabolism of macronutrients. Sufficient levels of Vitamin B12 can help optimize energy levels. However, it should not be considered a quick fix for energy issues, and underlying causes should be addressed as well.
D. Are there any natural food sources of Vitamin B12 for vegans?
While primarily found in animal-based foods, fortified plant-based foods such as fortified cereals, plant-based milk alternatives, and nutritional yeast can be valuable sources of Vitamin B12 for vegans.
E. What is the recommended daily dosage of Vitamin B12 for adults?
The recommended daily dosage of Vitamin B12 for adults is 2.4 micrograms (mcg). It is important to note that individual requirements may vary based on factors such as age, gender, and underlying health conditions. Consulting a healthcare professional is advisable for personalized recommendations.
F. Can Vitamin B12 deficiency be cured with dietary changes alone?
In some cases, mild deficiencies can be addressed with dietary changes and increased consumption of Vitamin B12-rich foods or fortified products. However, for more severe deficiencies or individuals with impaired absorption, supplementation or injections may be necessary. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for each individual case.
Related Topics Shocking Nutrition Facts That Will Change Your Diet Forever!









[…] Learn more about vitamin b12 in Vitamin B12: Everything You Need to Know […]
[…] Vitamin B12: Everything You Need to Know […]